The aneurysm
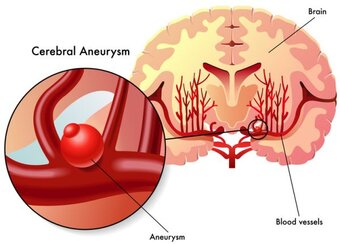
An aneurysm is a bulge of an artery that develops in most cases from a congenital weakness of the vascular wall.
Source: "aneurisma cerebrale" © rob3000 - fotolia
To visualize an aneurysm, special imaging techniques are needed. Sometimes the aneurysm can be presumed using a CT Scan or - even better - using a MRI scan. For a precise evaluation of the anatomy and further treatment options, however, a CT angiography or an convential angiography is required.
An aneurysm is either detected in a subarachnoid hemorrhage, ie, with the rupture of it or at the occurrence of neurological symptoms. An aneurysm can also be an incidental finding, discovered by performing a cross-sectional imaging for other reasons.
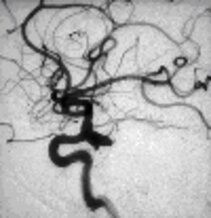
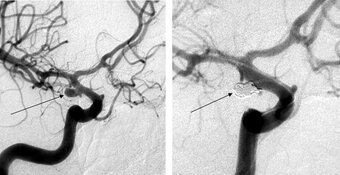
Left: Angiographic view of an aneurysm
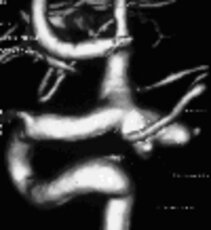
Right: Three-dimensional illustration of the same aneurysm
In the case of subarachnoid hemorrhage early treatment of the causing aneurysm is mandatory. If the aneurysm is discovered incidentally, the risks of treatment versus spontaneous course have to be weighed.
In our center, we use microsurgical clipping, as well as endovascular coil embolisation as treatment option. Depending on the anatomical configuration of the aneurysm and the comorbidities of the patient, the two treatment modalities are discussed and determined interdisciplinary for each patient individually by the departments of neurosurgery and neuroradiology .
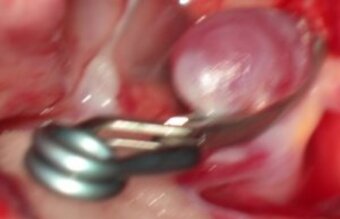
Aneurysm: The microsurgical treatment by clipping
Clipping is an open microsurgical surgery, a skull opening, called craniotomy is being performed under general anesthesia. Under the surgical microscope, the aneurysm is located and isolated from the supprt vessel with the help of a titanium clip. The bone flap is being reattached to the skull, the wound is being closed.
Advantage of the clipping: By clipping out the aneurysm under direct vision a control angiography is rarely necessary.
Disadvantage of clipping: The necessary opening of the skull.
Aneurysm: the neuroradiological treatment by coil embolisation
Coil embolisation is also performed under general anesthesia. A catheter is inserted through the femoral artery and advanced under fluoroscopy to the aneurysm-bearing artery. Subsequently, the aneurysm will be filled with platinum spirals, the so called coils, and therefore taken out of blood circulation.
Advantage of embolization: No opening of the skull required
Disadvantage of embolization: A coil compaction can occur later, therefor always a control angiography must be carried out, sometimes a re-treatment becomes necessary.
Treatment risks
are approximately equal for both methods and depend crucially on the location, size, configuration, and the anatomy of the aneurysm, but also on the age and the clinical condition of the patient.

Dr. Christian Scheiwe
Senior neurosurgeon
Consultation hours for vascular deseases

Dr. Mukesch Shah
Senior neurosurgeon