Our expertise
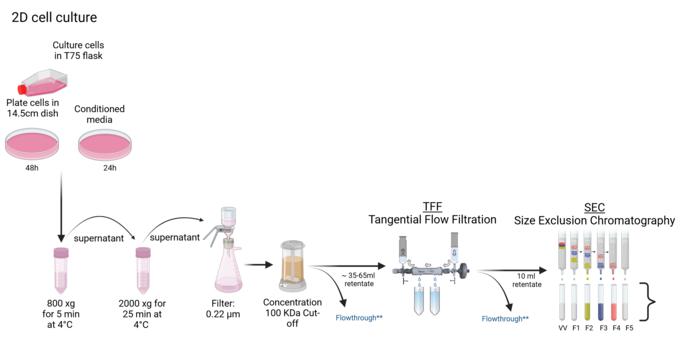
We specialize in isolating extracellular vesicles (EVs) from various sources, including cell cultures, organoids, bacteria, and body fluids. Our approach utilizes advanced Tangential Flow Filtration (TFF) techniques with the TFF Easy device, complemented by size-exclusion chromatography (SEC). This methodology allows us to obtain EVs of the highest purity and integrity, suitable for subsequent analytical purposes or characterization using a range of biochemical and molecular biology techniques.
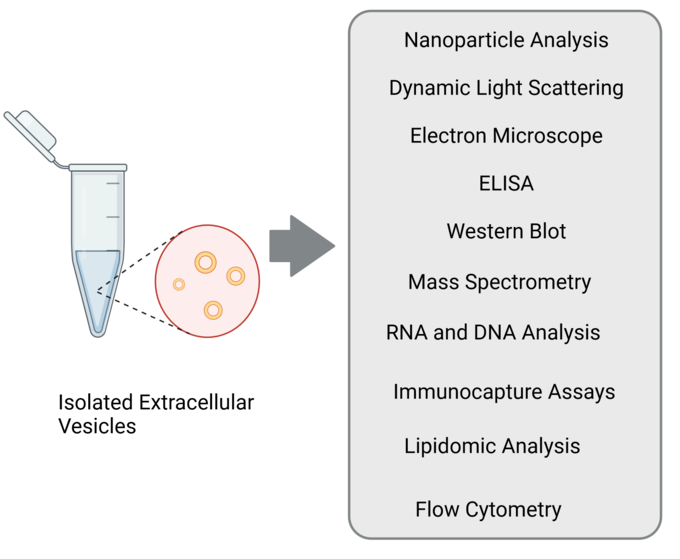
Characterizing EVs can be a complex process, and we often use a combination of the following techniques to obtain a comprehensive understanding of their properties and functions.
Size and Concentration Analysis
1. Single vesicle analysis
Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS): DLS measures the size distribution of EVs by analyzing how they scatter light as they move in a liquid. It provides information about the size distribution of vesicles.
Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA): NTA tracks individual EVs by analyzing their Brownian motion. It provides information about size distribution and concentration in certain size-ranges.
Flow NanoAnalyzer, nano-flow cytometry (nanoFCM): NanoFCM enables us multi-parameter analysis, to simultaneously measure particle concentration, size distribution, and biochemical properties of individual EVs. This level of detail is crucial, especially when studying complex and heterogeneous populations of nanoparticles, such as small EVs.
2. Fluorescent techniques for vesicle analysis
Fluorophore staining and membrane dye labeling: We use membrane dyes that selectively label EV membranes and fluorescent dyes which specifically bind to nucleic acids (RNA/DNA) present within the EVs.
Fluorescence analysis: After labeling the EVs with membrane dyes and staining them with fluorophores for concentration measurement, we analyze the samples using a flow cytometer or fluorescence microscope. Fluorescence microscopy allows detection of single EVs in real time, tracking their interaction and uptake within living cells.
Morphology
Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM): TEM allows for direct visualization of EVs at nanometer resolution, providing information about their shape and morphology. We work with the Core Facility for Electron Microscopy (EMcore) at the Medical Center – University of Freiburg led by Dr. Martin Helmstädter, which offers state-of-the-art TEM services for comprehensive EV analysis.
Protein Composition
1. Analysis of EVs' surface proteins
Bead-assisted flow cytometry: It is used to detect surface proteins on EVs by employing fluorescently labeled antibodies specific to the surface proteins of EVs.
Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence: It involves labeling EVs with fluorescently labeled antibodies specific to surface proteins of interest.
Multiplex protein profiling assays: They are utilized for the detection of surface proteins on EVs, enabling the simultaneous detection and quantification of multiple proteins within a single sample, offering a comprehensive approach to studying the protein composition of EVs.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA): ELISA can be adapted to detect surface proteins on EVs by immobilizing EVs on a solid-phase surface, such as a microplate well, and probing them with antibodies specific to the target surface proteins. The bound antibodies are then detected using enzyme-conjugated secondary antibodies and a chromogenic or chemiluminescent substrate.
Meso Scale Discovery (MSD) assays - Multiplex Assay Kits: We use flow cytometry kits for human EV which can detect up to 37 EV markers and 2 controls.
2. Total protein analysis
Western blotting (WB): WB is used to detect specific proteins on the surface or within EVs, helping to identify their origin and cargo.
Mass spectrometry (MS): Mass spectrometry is used to analyze the protein composition of EVs in a high-throughput manner, providing detailed information about their cargo. We work with the Proteomics Platform – Core Facility (ProtCF) at the Medical Center – University of Freiburg.
Protein arrays (Sciomics GmbH) are used to characterize surface proteins and cytokine content of EVs.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA): ELISA captures, detects, characterizes, and quantifies EVs/exosomes in human body fluids and cell culture supernatants.
Lipid Composition
Lipidomics: Lipidomic analysis can identify and quantify the lipid species present in EV membranes, providing insight into their lipid composition.
Nucleic Acid Analysis
RNA and DNA analysis: Techniques such as RT-qPCR and next generation RNA sequencing are used to analyze the RNA and DNA content of EVs, including microRNAs and other non-coding RNAs.
Functional Assays
Uptake studies: EV uptake by target cells are assessed using techniques like confocal microscopy, which can provide insights into their functional roles in intercellular communication.

Group leader
Prof. Dr. rer. nat. Irina Nazarenko
+49 (0) 761 270 82100
+49 (0) 761 270 82030
irina.nazarenko@uniklinik-freiburg.de
Institute for Infection Prevention and Control
Medical Center – University of Freiburg
Breisacher Straße 115 b, 79106 Freiburg im Breisgau, Germany
X (formerly Twitter): @nazarenkoteam
LinkedIn: Extracellular vesicles research group - Prof. Irina Nazarenko
Instagram: @nazarenkoteam
Assistance
Susanne Görner
Phone: +49 (0) 761 270 82390
Fax: +49 (0) 761 270 82030
susanne.goerner@uniklinik-freiburg.de