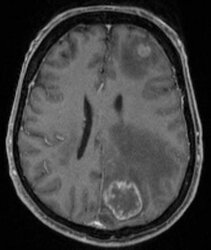
Metastases
What are metastases?
If individual tumor cells from tumors of other organs (primary tumors) reach the brain via blood brain metastases may develop. The most common brain metastases arise from primary tumors in the lung or breast. Their biological properties are similar to those of the primary tumor. Brain tumors usually develop no metastases in other tissues or organs.
What are the symptoms and what discomfort may occur?
Whether and what symptoms occur depends, among other things, on the location, size and growth rate of the metastasis.
The first symptoms are usually nonspecific, such as headaches, nausea, dizziness and/or circulatory problems. It may also be epileptic seizures, paralysis, impaired vision and aphasia.
What are the treatment options?
Brain metastases are treated by surgery, radiation and, rarely, chemotherapy.
Department of Neurosurgery
Neurocenter
Breisacher Str. 64
D-79106 Freiburg
Phone: +49 761 270-50010/-50020
Fax: +49 761 270-50240
neurochirurgie@uniklinik-freiburg.de