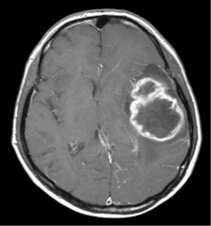
Glioma
What is a glioma?
Gliomas develop from the supporting cells of the brain. These cells are called glial cells. The types of gliomas derive from these types of glial cells. Astrocytomas, oligodendrogliomas or ependymomas are belong to the group of gliomas. Astrocytomas are the most common tumors.
The most aggressive type of glioma is glioblastoma (glioblastoma multiforme). It grows rapidly and invades the surrounding healthy brain.
In terms of their histological structure and growth behavior gliomas are classified in 4 grades (WHO I-IV) by the World Health Organization WHO .
When and how frequently do gliomas occur?
Gliomas are the most common brain tumors. Frequency and age when gliomas may occur vary depending on the type of glioma. Overall, gliomas occur in 2-3 patients per 100.000 inhabitants.
What are the symptoms and health problems caused by a glioma?
Symptoms depend on the loacation in the brain. Typical are headaches, vomiting, seizures, paralysis (hemiplegia/hemiparesis), speech impairment, visual impairment and brain disorders such as memory or concentration problems, etc. .
What are the treatment options?
For many gliomas a neurosurgical intervention is necessary, often supplemented by radiotherapy and chemotherapy. To prevent regrowth of the tumor, adjuvant treatment by chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy is performed.
Department of Neurosurgery
Neurocenter
Breisacher Str. 64
D-79106 Freiburg
Phone: +49 761 270-50010/-50020
Fax: +49 761 270-50240
neurochirurgie@uniklinik-freiburg.de