Experimental Radiology
Interventional MRIIn current interventional procedures, operations are mostly performed under X-ray or ultrasound image guidance. As MRI has many advantages over these classical imaging modalities (excellent soft tissue contrast, arbitrary image orientations, functional measurements), we realize advanced MRI concepts for MR-guided interventions in closed-bore high field MRI systems. During an intervention, minimally invasive access to the target organ is achieved either through the skin (percutaneous access) or via the blood vessels (intravascular access). For both access pathways we develop MR-compatible devices, we optimize imaging strategies to visualize the tissue morphology and the functional changes during therapy, and we test the new technologies in phantom and in vivo experiments.
Thomas Lottner, Simon Reiß, Simon Stephan, Ali C. Özen
MR-guided interventions might be beneficial for the patient, as they offer functional imaging during intervention (e.g., quantitative perfusion after stent placement in the coronary arteries). In this project we develop devices (active catheters, guidewires) and imaging methods (radial MRI) for visualizing and tracking of interventional equipment in the MR environment.
Successful engagement of the coronary artery with an active catheter with a loop coil on the tip of the catheter.
(click to view video)
References
- Özen, A. C., Silemek, B., Lottner, T., Atalar, E., & Bock, M. MR safety watchdog for active catheters: Wireless impedance control with real‐time feedback. Magn Reson Med. 2020 Aug; 84(2):1048-1060
- Heidt T, Reiss S, Lottner T, Özen AC, Bode C, Bock M, von Zur Mühlen C. Magnetic resonance imaging for pathobiological assessment and interventional treatment of the coronary arteries. Eur Heart J Suppl. 2020 Apr;22(Suppl C):C46-C56.
- Heidt T, Reiss S, Krafft AJ, Özen AC, Lottner T, Hehrlein C, Galmbacher R, Kayser G, Hilgendorf I, Stachon P, Wolf D, Zirlik A, Düring K, Zehender M, Meckel S, von Elverfeldt D, Bode C, Bock M, von Zur Mühlen C. Real-time magnetic resonance imaging - guided coronary intervention in a porcine model. Sci Rep. 2019 Jun 17;9(1):8663.
- von zur Mühlen C, Reiss S, Krafft AJ, Besch L, Menza M, Zehender M, Heidt T, Maier A, Pfannebecker T, Zirlik A, Reinöhl J, Stachon P, Hilgendorf I, Wolf D, Diehl P, Wengenmayer T, Ahrens I, Bode C, Bock M. Coronary magnetic resonance imaging after routine implantation of bioresorbable vascular scaffolds allows non-invasive evaluation of vascular patency. PLoS One. 2018 Jan 25;13(1):e0191413.
- Reiss S, Krafft AJ, Zehender M, Heidt T, Pfannebecker T, Bode C, Bock M, von Zur Muhlen C. Magnetic resonance imaging of bioresorbable vascular scaffolds: potential approach for noninvasive evaluation of coronary patency. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2015 Apr;8(4). pii: e002388.
- Schleicher KE, Bock M, Düring K, Kroboth S, Krafft AJ. Radial MRI with variable echo times: reducing the orientation dependency of susceptibility artifacts of an MR-safe guidewire. MAGMA. 2018 Apr;31(2):235-24
Cooperation Partners
- Cardiology and Angiology I, Heart Center, Freiburg University and Faculty of Medicine, Freiburg, Germany
- MaRVis Interventional GmbH, Frechen, Germany
Grant Support
- Originally funded by DFG BO 3025/11-1. Since July 2020 funded by the SFB 1425 (as sub-project P15).
Simon Reiß, Thomas Lottner, Ali C. Özen
A large variety of both active and passive medical implants consist of conductive materials that can be safety hazards during MRI due to RF heating. In addition, the growing field of MR-guided intervention necessitates the use of active instruments which also cause potential sources of RF heating. In this project we develop novel methods to assess and reduce RF-induced heating of active and passive medical devices.
a) Comparison of the theoretically determined and measured electric field in the vicinity of a vascular stent. The results compare well to the temperature increase during RF induced heating measured with MR thermometry. b) Time course of the temperature increase at the tip of the stent during MR imaging.
References
- Reiss, S., Lottner, T., Özen, A. C., Polei, S., Bitzer, A., Bock, M. (2020). Analysis of the RF Excitation of Endovascular Stents in Small Gap and Overlap Scenarios using an Electro-optical E-field Sensor. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering.
- Erhardt J. B., Lottner T., Pasluosta C. F., Gessner I., Mathur S., Schuettler M., Bock M., Stieglitz T. Fabrication and validation of reference structures for the localization of subdural standard- and micro-electrodes in MRI. J Neural Eng. 2020 Sep 18;17(4):046044.
- Özen, A. C., Silemek, B., Lottner, T., Atalar, E., & Bock, M. MR safety watchdog for active catheters: Wireless impedance control with real‐time feedback. Magn Reson Med. 2020 Aug; 84(2):1048-1060
- Erhardt, J. B., Lottner, T., Martinez, J., Özen, A. C., Schuettler, M., Stieglitz, T., Ennis, Daniel B., & Bock, M. (2019). It's the little things: On the complexity of planar electrode heating in MRI. NeuroImage, 2019 Jul; 195, 272-284.
- Özen, A. C., Lottner, T., & Bock, M. Safety of active catheters in MRI: Termination impedance versus RF‐induced heating. Magn Reson Med., 2018 Oct; 81(2), 1412-1423.
- Reiss, S., Bitzer, A., & Bock, M. An optical setup for electric field measurements in MRI with high spatial resolution. Physics in Medicine & Biology, 2015 May; 60(11), 4355.
Cooperation Partners
- CORTRONIK GmbH, Rostock-Warnemunde, Germany
- Dr. Andreas Bitzer, Institute of Photonics and ICT (IPI), University of Applied Sciences FHGR, Chur, Switzerland
- Prof. Ergin Atalar, Bilkent Univ., Ankara, Turkey
- Dr. Berk Silemek, PTB Berlin
Grant Support
Katharina Schleicher, Axel J. Krafft
In MRI, labeling of interventional instruments is often realized with iron oxides which are non-toxic and which can create large signal voids even at low concentrations. Recently, iron oxides have been used as markers in MR-safe intravascular guidewires – unfortunately, the markers appear as dipole artifacts in the MR image. To overcome the orientation-dependence of the dipole artifact, a dedicated radial MRI technique was developed which varies the echo time (TE) as a function of the orientation of the radial spoke against the direction of the static magnetic field B0.
Top: Fiber-based guidewire with iron oxide markers that cause field distortions with a characteristic dipole shape. Bottom: Conventional Cartesian or radial sampling leads to strong variation of the artifact size with the orientation angle, whereas the new TE-modulated radial acquisition (sin² TE) is less angle-dependent. From: Schleicher KE, et al. MAGMA 31(2):235-242 (2018)
References
- Schleicher KE, Bock M, Düring K, Kroboth S, Krafft AJ. Radial MRI with variable echo times: reducing the orientation dependency of susceptibility artifacts of an MR-safe guidewire. MAGMA 31(2):235-242 (2018)
Cooperation Partners
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) as a noninvasive imaging technique offers unique advantages over computed tomography or ultrasound imaging for interventional procedures. MRI has an excellent soft tissue contrast, provides morphological imaging in arbitrary scan planes and enables functional imaging without the application of ionizing radiation. Unfortunately, closed-bore magnets severely limit the patient access and often do not offer a direct line of sight to the interventional instrument. To overcome these limitations, we combine small assistance systems with real-time instrument tracking sequences to facilitate interventional procedures in closed-bore MR systems, for example to perform MR-guided prostate biopsies.
Top: A small, patient-mounted assistance system (GantryMate) for MR-guided needle interventions [2]. Bottom: Automatic image plane alignment with a targeted region (yellow circle). The passive marker needle guide is automatically detected with a phase-only cross correlation (POCC) algorithm which enables real-time targeting maneuvers [1].
References
- Reichert A, Reiss S, Krafft AJ, Bock M. Passive needle guide tracking with radial acquisition and phase-only cross-correlation. Magn Reson Med. 2020 Aug 7.
- Reichert, A., Bock, M., Reiss, S. et al. Simultaneous slice excitation for accelerated passive marker tracking via phase-only cross correlation (POCC) in MR-guided needle interventions. Magn Reson Mater Phy (2018) 31: 781.
- Reichert A, Bock M, Vogele M, Joachim Krafft A. GantryMate: A Modular MR-Compatible Assistance System for MR-Guided Needle Interventions. Tomography. 2019;5(2):266–273.
Cooperation Partners
Grant Partners
- Tiroler Innovationsförderung (Project “GantryMate”)
- ZIM/IraSME
Temperature measurement methods have been designed for MR-guided hyperthermia in tumor patients (Cooperation with J. Gellermann and O. Voigt/Univ. Tübingen)
Dadakova T, et al. Fast PRF-based MR Thermometry Using Double-Echo EPI: In Vivo Comparison in a Clinical Hyperthermia Setting. Magn Reson Mater Phy 2014, Nov 8. [Epub ahead of print]
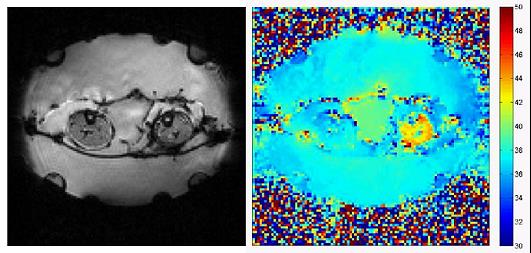
Temperature map during a hyperthermia treatment in patient with a myxoid liposarcoma in the left leg – the local temperature increase in the tumor can be clearly identified.
To accelerate the image acquisition during MR-guided intravascular procedures, novel image acquisition and reconstruction technologies are investigated, which utilize data from a limited number of projections to reconstruct vascular trees in real time (DFG project BO 3025/2-1 and /2-2)
Brunner A, et al. An MR-compatible stereoscopic in-room 3D-display for MR-guided interventions. Magn Reson Mater Phy 2014;27(4):277-282
For MR-guided prostate therapies, temperature measurement technologies and radio-frequency coil systems have been developed to perform high intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) therapies with novel therapeutic US transducers (EUROSTARS project PROFUS, closed)
Yiallouras C, et al. Three-axis MR-conditional robot for high-intensity focused ultrasound for treating prostate diseases transrectally. J Ther Ultrasound 2015;3:2
To enable intravascular interventions, novel MR-safe guidewires are investigated, and optimized imaging strategies are presented in order to be able to visualize the guidewires with variable contrasts (Cooperation with MarvisTech)
Prof. Dr. Michael Bock
Director of Experimental Radiology
Tel.: +49 761 270-94140
E-Mail: michael.bock@uniklinik-freiburg.de
University Medical Center Freiburg
Dept. of Radiology · Medical Physics
Killianstr. 5a
79106 Freiburg
Oksana Chikh
Administrative Assistant
Tel.: +49 761 270-93840
E-Mail: oksana.chikh@uniklinik-freiburg.de